Build Your Career
with Confidence
Your success story begins here.
My Career Advisor Supports Job Seekers

My Career Advisor Supports Job Seekers
-
Increased chances of getting hired: A well-designed and clearly organized resume increases chances of getting noticed by employers.
-
Greater confidence: Access to career development resources can help our job seekers feel more confident in their abilities and better prepared for new challenges.
-
More opportunities: Employees who enhance their existing skills and developing new ones have better job opportunities in the long run.
My Career Advisor Supports Young Adults

My Career Advisor Supports Young Adults
-
Job Preparation: We offer career development resources to help students work towards their professional goals.
-
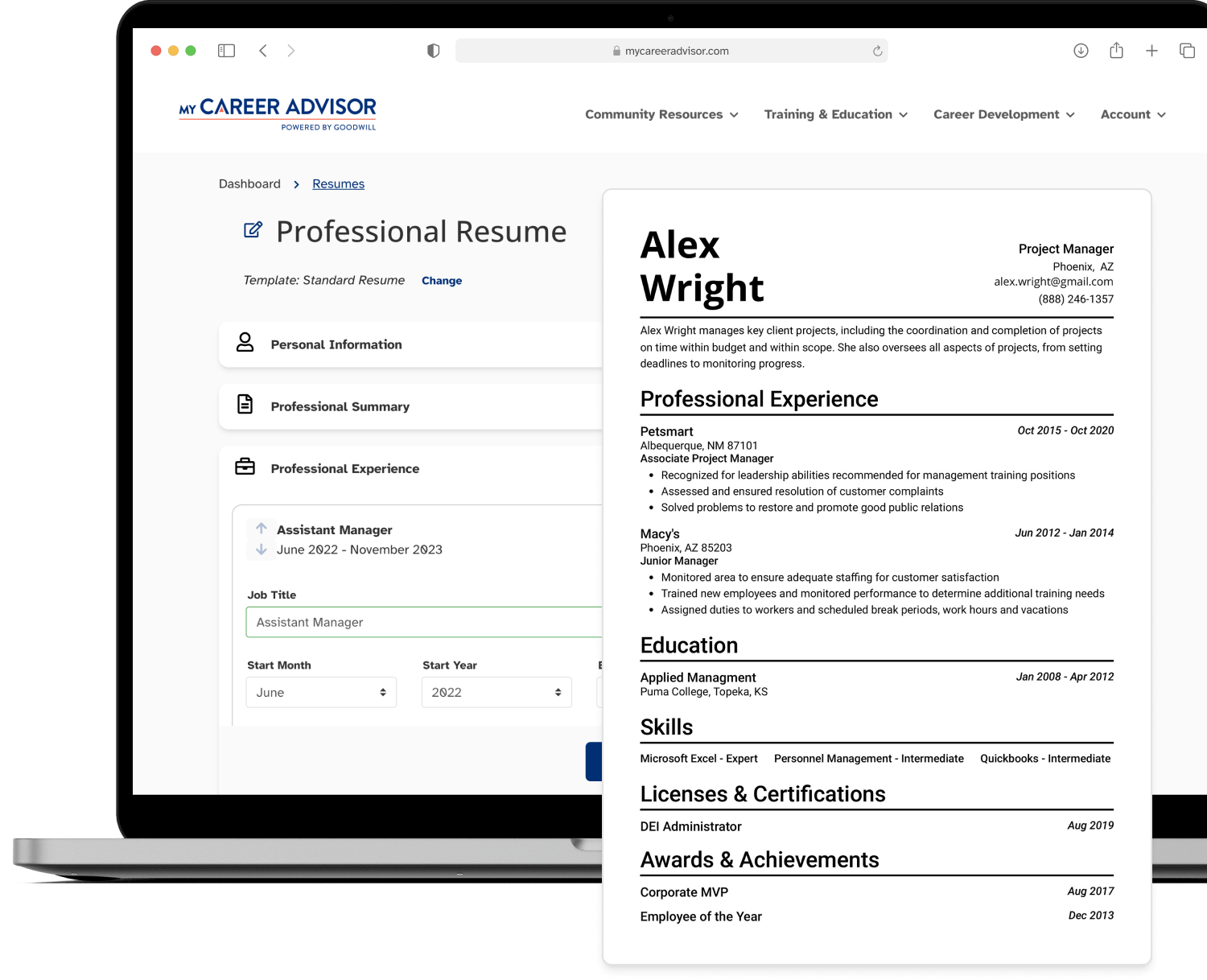
Resume Creation: Our guided resume builder has a template specifically designed for high school students.
-
Skills Training: Students can improve their interview skills and financial knowledge with our online trainings.
My Career Advisor Supports Our Veterans

My Career Advisor Supports Our Veterans
-
Seamless Transition: We provide tools to facilitate a seamless transition into civilian roles.
-
Tailored Resume: Our resume builder allows veterans to easily translate their military experience on to a traditional resume.
-
Resources: My Career Advisor has a curated list of veteran specific resources to help with re-entering into the job market.

Overall, the MCA training courses have helped me transform my life.
The most important thing I’ve learned is that while a job is temporary, a career is for a lifetime. I’m finally in a place where I can start to consider that as a possibility for me. Thanks to the skills and support I received through Goodwill’s Career Center and training opportunities, I’m no longer just living day to day. I’m discovering what happiness and success mean to me, looking at what my future could be, and opening new doors of opportunity.
Clifford Curry
My Career Advisor User, Army Veteran and Proud Father
My Career Advisor has tools that help with:
Skills Training
Learning new skills makes job seekers better equipped to perform their jobs more efficiently and effectively.

Career Development
Enhancing existing skills and developing new ones lead to better job opportunities.
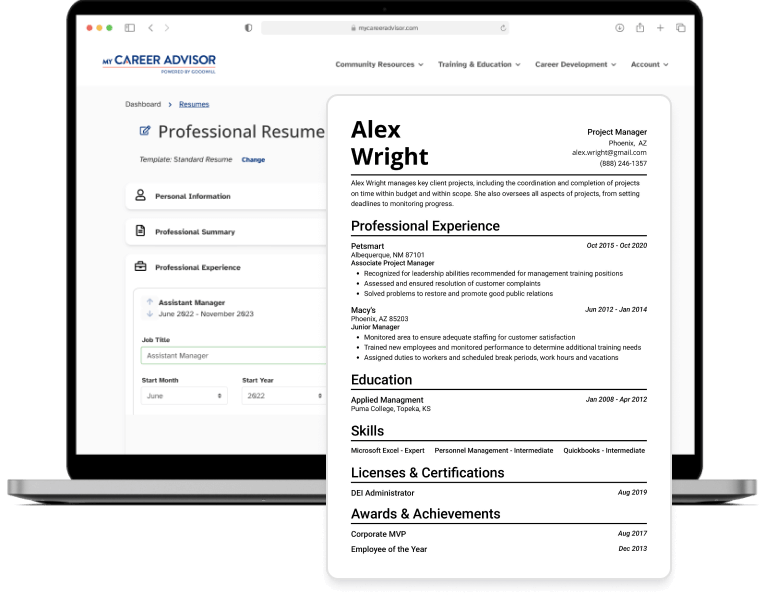
Resume Creation
A well-designed and clearly organized resume increases chances of getting noticed by employers.
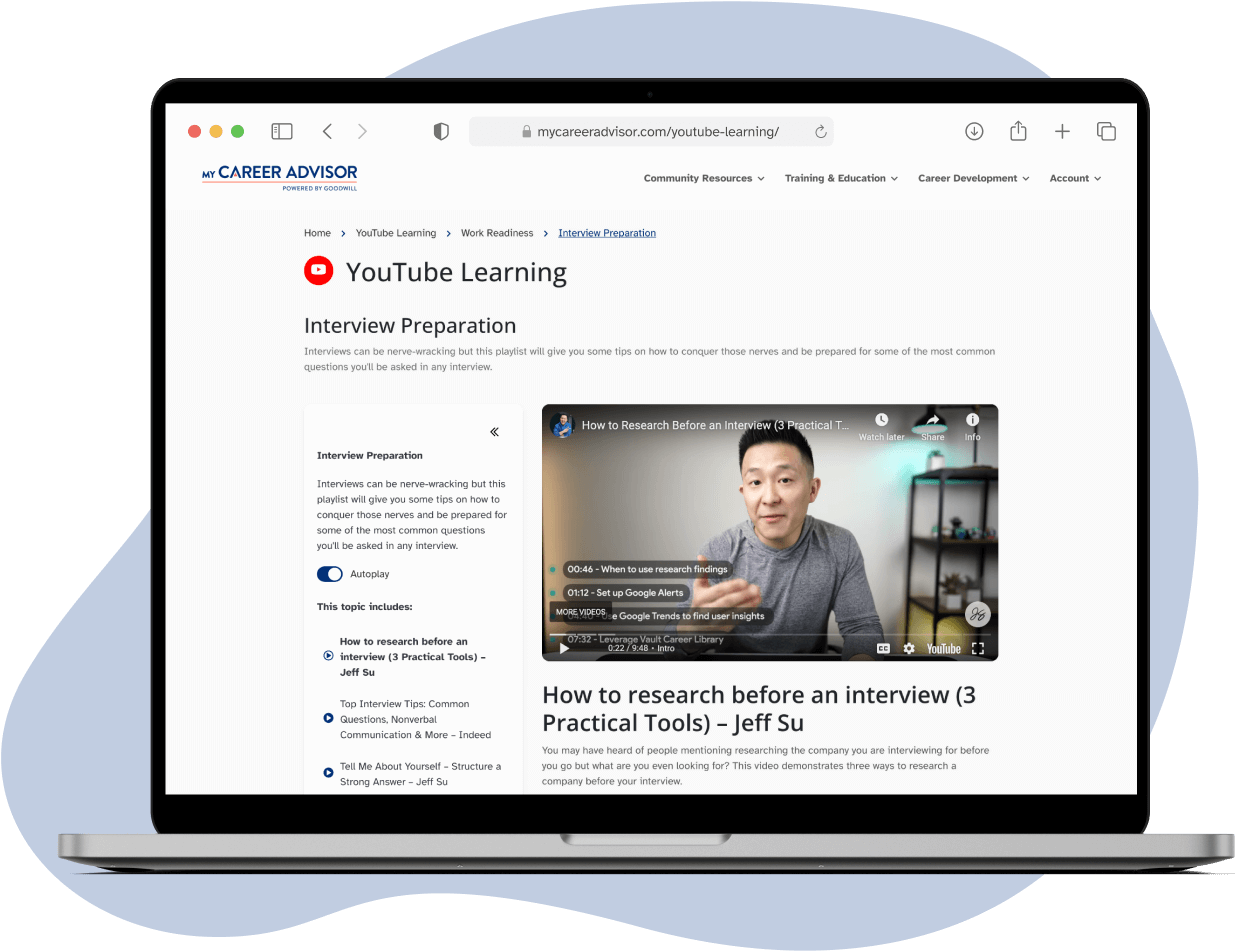
Take a look at our extensive video library in our YouTube Learning section!
Our YouTube Learning section has curated playlists of many topics such as applying to college, exploring a career, and finding what area of the military would fit you best.